Static rules allow you to define the composition form of the website URL according to your actual needs.
To facilitate users and reduce the trouble of configuration, the system is built-in with 4 ready-made pseudo-static rules that can be directly used by simply selecting them.
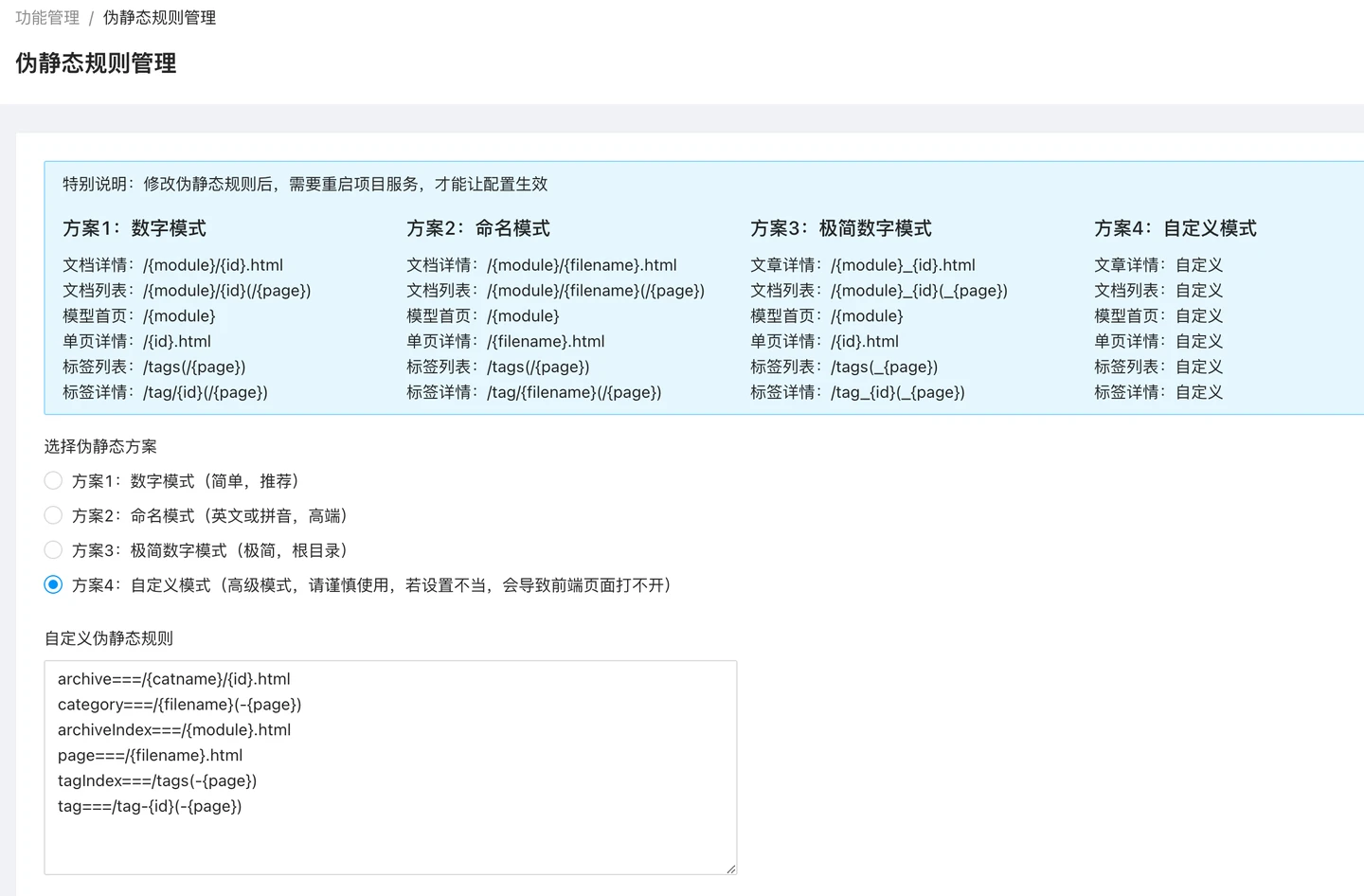
The default rewrite rules are:
- The document details, document list, single page details, document tags, all use {id} as the basis for URL generation, which is commonly used for Chinese websites.
- Model naming pattern, generally used for English websites
- Category naming pattern 1, generally used for Chinese websites
- Category naming pattern 2, category naming pattern 1, generally used more on English websites
In order to allow you to customize the link display format of the website content, the system also provides a custom mode.
Custom mode belongs to the advanced mode. In actual use, please be sure to configure it according to the requirements, otherwise it may cause the page to not open.
The custom static rules pattern can be set to 6 groups of static rules, each corresponding to different pages, including document details, document list, model homepage, page, tag list, and tag details.===And the preceding part cannot be modified.
In the custom rules, some available rules have been listed, you can copy these rules to further modify them to meet your needs.
As for the rule:
archive===/{module}-{id}.html
category===/{module}-{filename}(-{page})
archiveIndex===/{module}.html
page===/{filename}.html
tagIndex===/tags(-{page})
tag===/tag-{id}(-{page})
In the actual rule configuration, each rule is composed of规则名===规则值paired with. Rule names include:archive/category/archiveIndex/page/tagIndex/tag.
In the rule values, there are some commonly used variables that can be selected and used. Variables are enclosed in curly braces{}For example,{id}Available variables: Data ID{id}, Data custom link name{filename}, Category custom link name{catname}, Category ID{catid}, Model table name{module}Page number{page}Page number should be placed within parentheses, like:(/{page}).

By combining variables, you can generate some complex URL pseudo-static forms.

